

Beibei Wang, Rachel Sexton, Michael Feig
BBA - Gene Regulatory Mechanisms (2017), 1860, 482-490
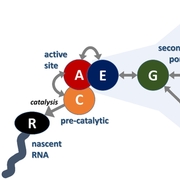
During transcription, RNA polymerase II elongates RNA by adding nucleotide triphosphates (NTPs) complementary to a DNA template. Structural studies have suggested that NTPs enter and exit the active site via the narrow secondary pore but details have remained unclear. A kinetic model is presented that integrates molecular dynamics simulations with experimental data. Previous simulations of trigger loop dynamics and the dynamics of matched and mismatched NTPs in and near the active site were combined with new simulations describing NTP exit from the active site via the secondary pore. Markov state analysis was applied to identify major states and estimate kinetic rates for transitions between those states. The kinetic model predicts elongation and misincorporation rates in close agreement with experiment and provides mechanistic hypotheses for how NTP entry and exit via the secondary pore is feasible and a key feature for achieving high elongation and low misincorporation rates during RNA elongation.